When Deep Learners Change Their Mind: Learning Dynamics for Active Learning
Published in CAIP, 2021
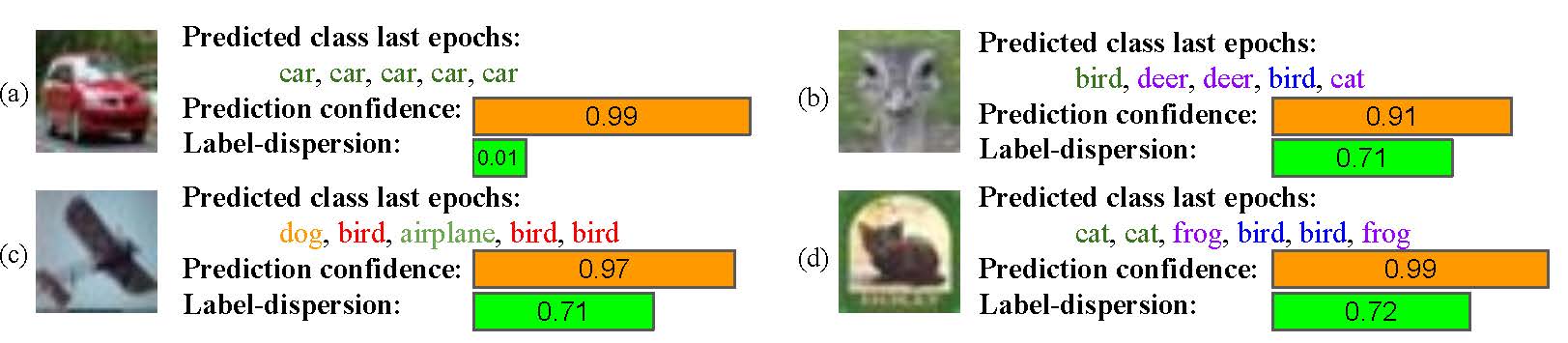
To tackle the overconfidence of neural nets, we introduce dispersion metric that is based on learning dynamics of neural nets. [Paper][Video]
Abstract:
Active learning aims to select samples to be annotated that yield the largest performance improvement for the learning algorithm. Many methods approach this problem by measuring the informativeness of samples and do this based on the certainty of the network predictions for samples. However, it is well-known that neural networks are overly confident about their prediction and are therefore an untrustworthy source to assess sample informativeness.
In this paper, we propose a new informativeness-based active learning method. Our measure is derived from the learning dynamics of a neural network. More precisely we track the label assignment of the unlabeled data pool during the training of the algorithm. We capture the learning dynamics with a metric called label-dispersion, which is low when the network consistently assigns the same label to the sample during the training of the network and high when the assigned label changes frequently.
We show that label-dispersion is a promising predictor of the uncertainty of the network, and show on two benchmark datasets that an active learning algorithm based on label-dispersion obtains excellent results.
